Seeding in hTau mice
Tauopathies share the pathogenic process of hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of the microtubule associated protein tau (MAPT) which gets more and more into researcher’s focus. By injecting fractions of Alzheimer’s disease patients’ brain tissue into the brain of transgenic tau mice, the tauopathy-specific phenotype can be accelerated, closely mimicking tau phosphorylation and spreading in humans.
hTau mice, expressing human tau while murine tau is deleted, are stereotactically injected into the right dorsal hippocampus with the sarkosyl insoluble fraction from Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue (AD seeds) or vehicle. Twelve weeks after surgery, animals are euthanized and brain tissue histologically evaluated for phosphorylated tau.
The most important characteristics of hTau mice injected with AD seeds are:
- Tau phosphorylation at residues Ser202/205, Thr231, Tyr18, and Ser396
- Tau spreading

Figure 1: Tau phosphorylation at residues Ser202/Thr205, Thr231, Tyr18, and Ser396 in the hippocampus of hTau mice injected with AD seeds. pSer202/Thr2025 (A), pThr231 (B), pTyr18 (C), and pSer396 (D) Immunoreactive area in the contra- and ipsilateral hippocampus of hTau mice injected with AD seeds compared to vehicle-injected hTau mice. Mean + SEM; Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test. n = 8 per group. *p <0.05; ***p <0.001.
Scantox offers a custom-tailored study design for the hTau mouse treated with AD seeds, and we are flexible to accommodate to your special interest. We are also happy to advise you and propose study designs. The hTau mouse injected with AD seeds shows a relevant tau-related phenotype shortly after treatment. This grants a remarkable fast processing time of your tauopathy study. Furthermore, vehicle-injected hTau mice can serve as control needed for proper study design.
We are happy to evaluate the efficacy of your compound in the hTau mouse injected with AD seeds! The most common readouts are:
- Tau phosphorylation at several residues
- Tau spreading
You might also be interested in these related topics:
- hTau Transgenic Mouse Model
- PS19 Transgenic Mouse Model
- AAV9 tau P301L-induced tau seeding
- In vitro Alzheimer’s disease models
x
Hypothermia-Induced Tau Phosphorylation
Accumulation of phosphorylated tau (ptau) protein is a characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease, tauopathies and many other neurodegenerative diseases. Hyperphosphorylated tau was shown to dissociate from microtubuli, resulting in the breakdown of the axonal flow, and thus impairing neuronal viability and function. Since tau presents a promising drug target, tau phosphorylation by hypothermia provides a quick tool for the analysis of drug effectiveness.
Adult male wild type mice were anesthetized with vaporized isoflurane and either placed at room temperature to induce hypothermia or on a heating pad and covered to keep body temperature stable. Animals were kept under anesthesia for 60 minutes. Animals of the hypothermia group presented a significantly reduced body temperature starting 10 minutes after anesthesia induction while animals of the normothermia group showed only a minor reduction of the body temperature (Figure 1).
The most important characteristics of hypothermia-induced tau phosphorylation mice are:
- Unchanged total tau levels
- Increased ptau Ser202/Thr205 of the 3R and 4R isoforms
- Increased ptau Ser396 levels
- Increased ptau Thr217 of the 4R isoform

Figure 1: Body temperature before and after induction of hypothermia in wild type mice. Animals were anesthetized and kept normothermal or hypothermalfor 60 minutes. Body temperature was measured every 10 minutes. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. n=8 per group. Mean ± SEM. ***p<0.001.
After 60 minutes under anesthesia, all animals were sacrificed, and hippocampal tissue of all mice was collected and evaluated for total tau by automated western blotting (WES™) and ptau Ser202/Thr205 levels by western blotting. Results show unaltered total tau levels (Figure 2A) but significantly increased ptau Ser202/Thr205 levels of the 3R and 4R tau isoforms (Figure 2B, C). Evaluation of ptau at residue Ser396 by WES™ also resulted in significantly increased ptau Ser396 levels (Figure 2D). Further evaluation of ptau at residue Thr217 by western blotting resulted in significantly increased ptau Thr217 levels of the 4R tau isoform (Figure 2F) while no changes could be observed for the 3R tau isoform (Figure 2E).

Figure 2: Total tau, ptau Ser202/Thr205, ptau Ser396 and ptau Thr217 levels in the hippocampus of wild type mice 1 hour after induction of hypothermia. Total tau by WES (A), ptau Ser202/Thr205 of two tau isoforms, 3R (B) and 4R (C), by western blotting, ptau Ser396 (D), and ptau Thr217 of two tau isoforms, 3R (E) and 4R (F)were quantified. Unpaired t-test.n=8 per group, Mean + SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
The in vivo hypothermia model allows a rapid evaluation of tau phosphorylation at several residues. The 3R and 4R tau isoforms can be quantified separately by standard western blotting or automated western blotting WES™.
Scantox offers a custom-tailored study design for the hypothermia-induced tau phosphorylation mouse model, and we are flexible to accommodate to your special interest. We are also happy to advise you and propose study designs. The hypothermia-induced tau phosphorylation mouse model shows a relevant tau phosphorylation phenotype already 60 minutes after induction of hypothermia. This grants a remarkable fast processing time of your tau study. Furthermore, wild type mice kept normothermal can serve as control needed for proper study design.
We are happy to evaluate the efficacy of your compound in the hypothermia-induced tau phosphorylation mouse model! The most common readouts are:
You might also be interested in these related topics:
a
Scopolamine-treated Rats
Scopolamine is a tropane alkaloid drug with a competitive antagonistic effect on muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR). Systemic application of scopolamine disrupts the performance in several reference memory tasks, such as object discrimination, radial arm maze, Morris water maze and fear conditioning in rats. The scopolamine-induced memory impairment can be reversed by cholinesterase inhibitors. This model can thus be used to mimic memory dysfunction observed in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Furthermore, it is a useful initial screening tool to identify therapeutic candidates for learning and memory deficits.
The most important characteristics of scopolamine-treated rats are:
- Memory deficits
Treatment of Wistar rats with scopolamine causes a reduced latency to enter the dark compartment in the passive avoidance test. This reduced cognitive function can be reversed by methylphenidate treatment (Figure 1).
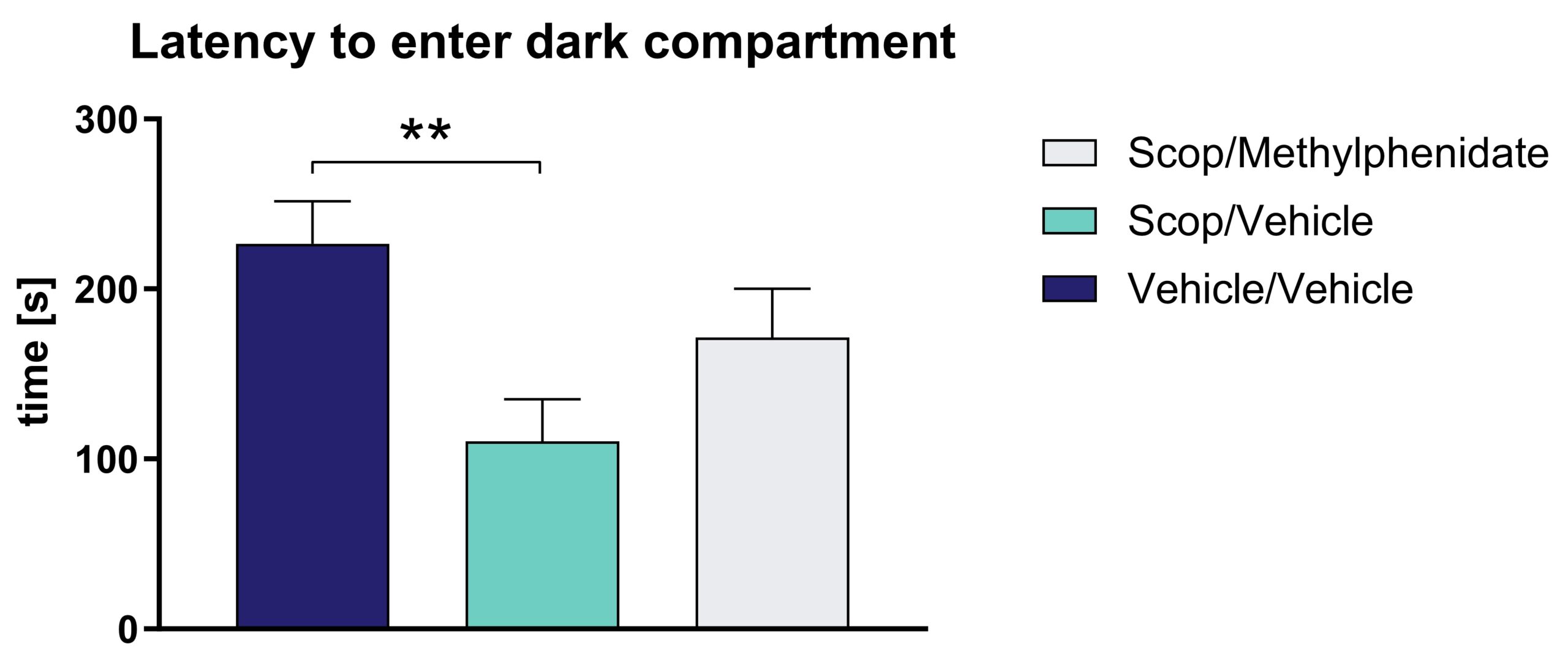
Figure 1: Effect of scopolamine (Scop) on passive avoidance response of Wistar rats. Latency to enter the dark compartment. The effect of scopolamine can be reduced by methylphenidate treatment. Mean ± SEM; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn`s multiple comparison test. n = 12 per group; **p<0.01.
Scantox offers a custom-tailored study design for the scopolamine-induced rat model, and we are flexible to accommodate to your special interest. We are also happy to advise you and propose study designs. The scopolamine-treated rat model shows a relevant memory related phenotype very shortly after treatment. This grants a remarkable fast processing time of your memory study. Furthermore, vehicle-injected wild type rats can serve as control needed for proper study design.
We are happy to evaluate the efficacy of your compound in the scopolamine-treated AD rat model! The most common readout is:
- Memory deficits that can be evaluated by different behavioral tests


