Studies to Assess Efficacy or Safety of Wound Treatments
Since 2004, Scantox has performed wound healing studies in rats and minipigs. The wound healing studies are conducted to investigate safety, toxicity, and bioavailability of wound dressings, formulations, dermal patches, etc.
Wound healing studies have also been conducted to assist during the early development of formulations and medical devices. At Scantox, both full thickness and split thickness (partial thickness) wound healing studies are performed.
Split thickness wounds
In split-thickness wounds, the epidermis and the upper part of the dermis is removed by a dermatome. Split-thickness wounds are used as models for more superficial wounds. Healing occurs by re-epithelialisation from the wound-edges and the hair follicles. During the healing period, the wounds are evaluated at suitable timepoints.
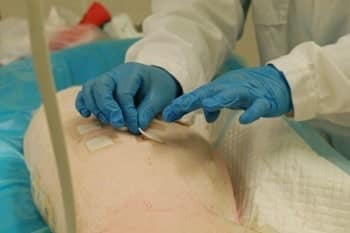
Full thickness wounds
In full thickness wound healing studies, the epidermis, dermis, and subcutis are removed using a specially designed round knife. The wounds heal by contraction, granulation, and re-epithelialisation, followed by remodelling of the granulation tissue beneath the re-epithelialised wound surface.
Full-thickness wounds are used as models for treatment of open wounds. During the healing period, the wounds are evaluated at suitable timepoints.
