Scantox provides fast and reproducible screening assays to investigate if your developmental compounds are able to protect against cytotoxic effects of aggregated Aβ1-42. Various in vitro models from primary neurons to several cell lines are available and described on the following pages.
Primary rat and mouse neurons
The hippocampus, a brain area critical for learning and memory, is especially vulnerable to damage at early stages of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Primary rat/mouse hippocampal neurons are phenotypically closer to adult neurons as they have extended a dense network of neuronal processes.
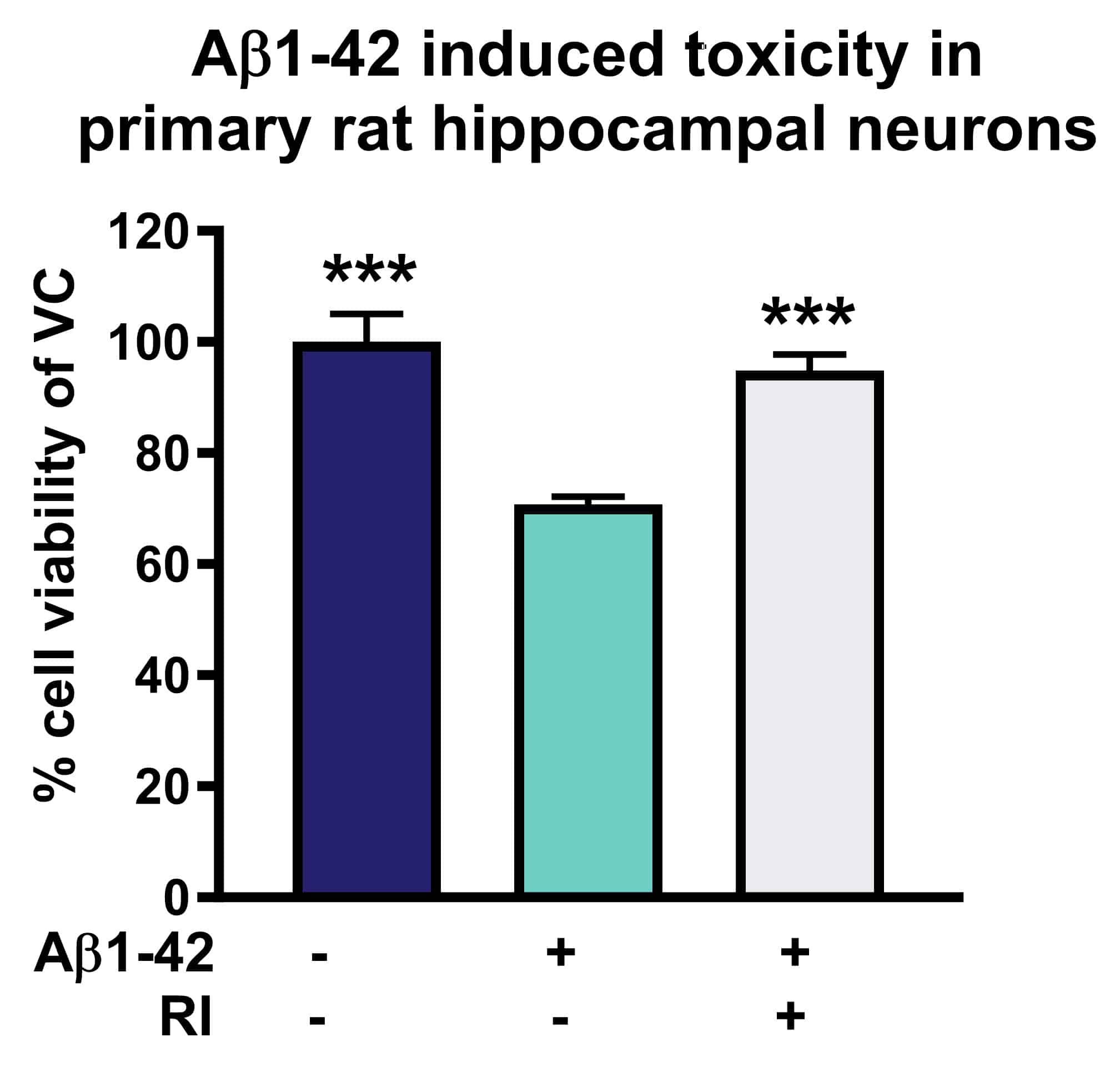
Figure: Neuroprotective effects of RI on Aβ1-42 induced toxicity in primary rat hippocampal neurons. Vehicle control, aggregated Aβ1-42 [1µM, 48h] or Reference item (RI) with aggregated Aβ1-42 were applied to primary rat hippocampal neurons. After 144h, cell viability was determined according to MTT assay. RI rescued cell viability and protected against toxic effects of Aβ1-42.
SH-SY5Y cells
SH-SY5Y cells is a human derived neuroblastoma cell line and has become a popular in vitro model for neurodegenerative diseases.
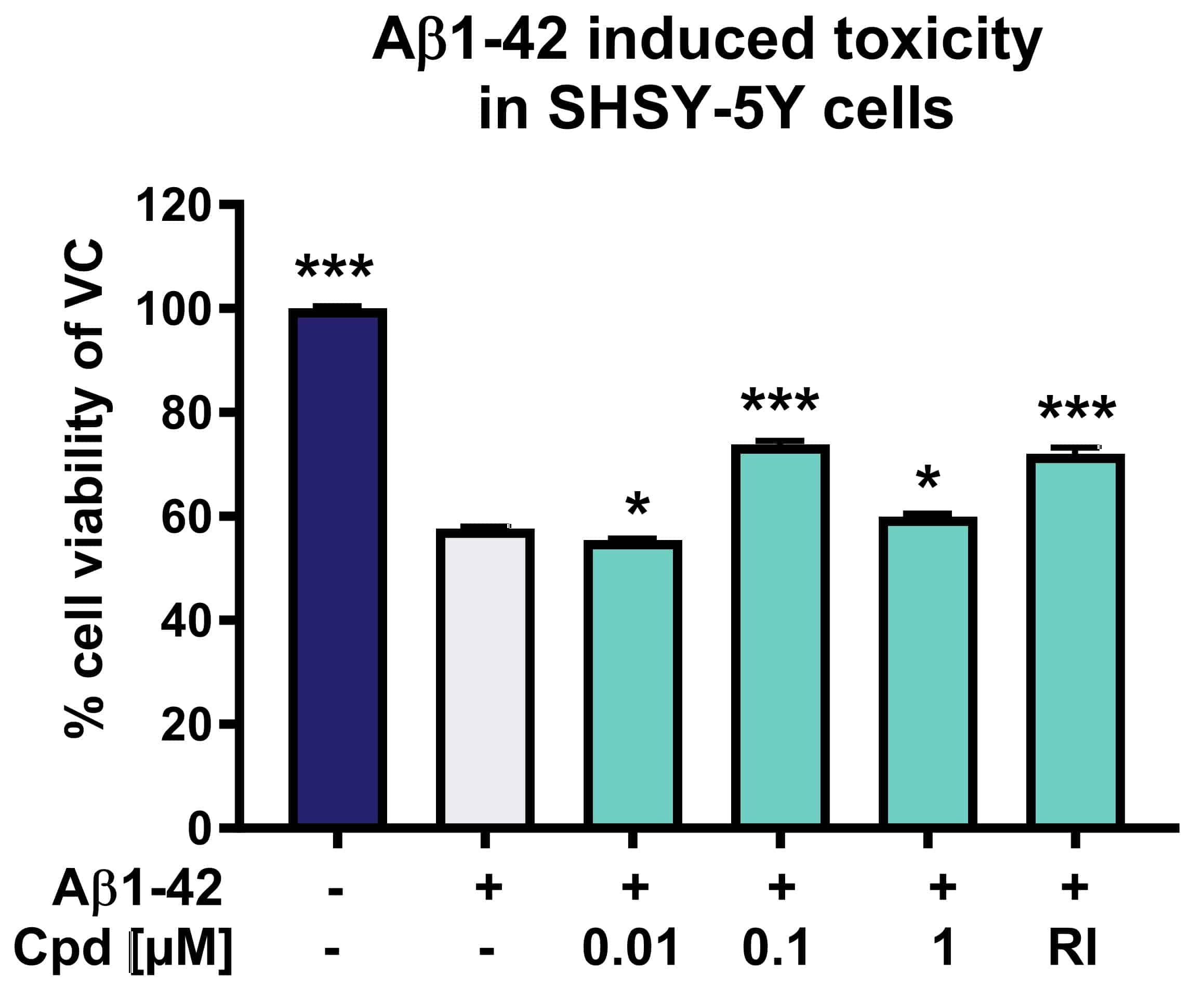
Figure: Evaluation of neuroprotective effects of compounds on Aβ induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Compounds were applied together with aggregated Aβ1-42 (1 µM) to SH-SY5Y cells for 96h. Cell viability was determined according to MTT assay. Reference item and Compound X (at 0.1 and 1µM) were able to protect against toxic effects of Aβ1-42.
More cell lines
Aβ1-42 toxicity assay is also available in:
- ARPE-19 cells (human Retina Pigment Epithelial cell line)
- PD cells (human fibroblasts from a PD patient)
- FRDA cells (human fibroblasts from a Friedreich Ataxia patient)
- LHON cells (human fibroblasts from a Leber‘s hereditary Optic Neuropathy)
