Newest results of our R&D team show highly increased total and phosphorylated tau (ptau) levels in transgenic PS19 mice already at early age. This rodent model for tauopathies expresses the T34 isoform and 4 microtubule binding repeats (1N4R) of the tau protein with P301S mutation under the regulatory control of the murine prion promoter (Prnp). So far, animals are published to present increased ptau levels at the age of 6 months. We now present data, showing that PS19 have already highly increased total and ptau231 levels at the age of 2.5 months, making the PS19 mouse an early model of tauopathies and probably decreasing the time needed to perform efficacy studies.
Analysis of the cortex of 2.5, 4.5, 6.5, and 8 months old PS19 mice showed highly increased total tau and ptau231 levels compared to non-transgenic (ntg) littermates in the soluble cortical fraction (Fig.1A, B). While total tau levels of PS19 mice significantly increased with age (Fig.1A), were ptau231 levels already highly increased in all age groups and did not change with age (Fig.1B). Evaluation of the insoluble cortical fraction of PS19 mice showed similar results as observed in the soluble fraction (Fig.1C, D), although total tau levels in the insoluble cortical fraction of PS19 mice decreased with age (Fig.1C).
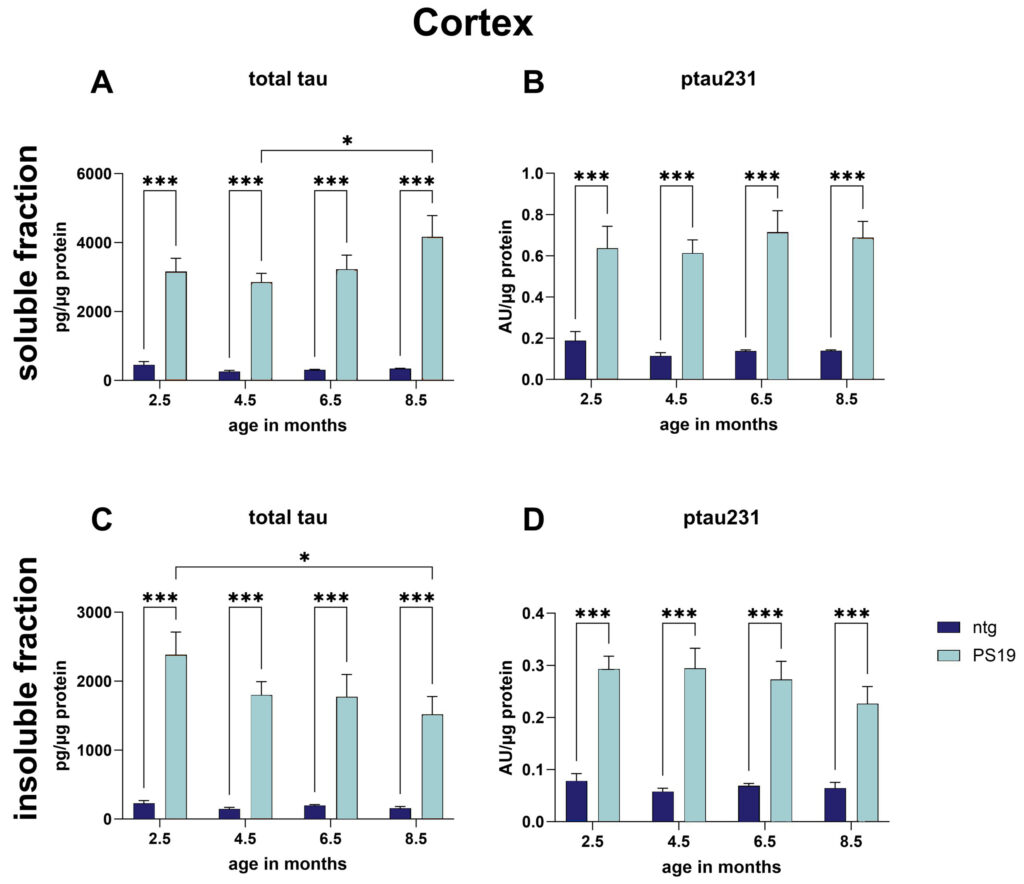
Figure 1: Total tau and ptau231 levels in the soluble and insoluble cortical fraction of PS19 and ntg mice at the age of 2.5, 4.5, 6.5, and 8 months. Immunosorbent assay for total tau and ptau231 in Triton X-100 soluble and insoluble fraction. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test. Mean + SEM; n = 8 / group; *p<0.05; ***p<0.001.
Evaluation of the soluble hippocampal fraction of 2.5, 4.5, 6.5, and 8 months old PS19 mice showed highly increased total tau and ptau231 levels at the age of 8 months compared to ntg littermates as well as younger PS19 mice (Fig.2A, B). Analysis of total tau in the insoluble hippocampal fraction showed similar results as observed in the soluble fraction (Fig.2C). ptau231 levels in the insoluble hippocampal fraction were already significantly increased at the age of 2.5 months compared to ntg littermates. Additionally, hippocampal ptau231 levels increased even further with age in this insoluble fraction (Fig.2D).
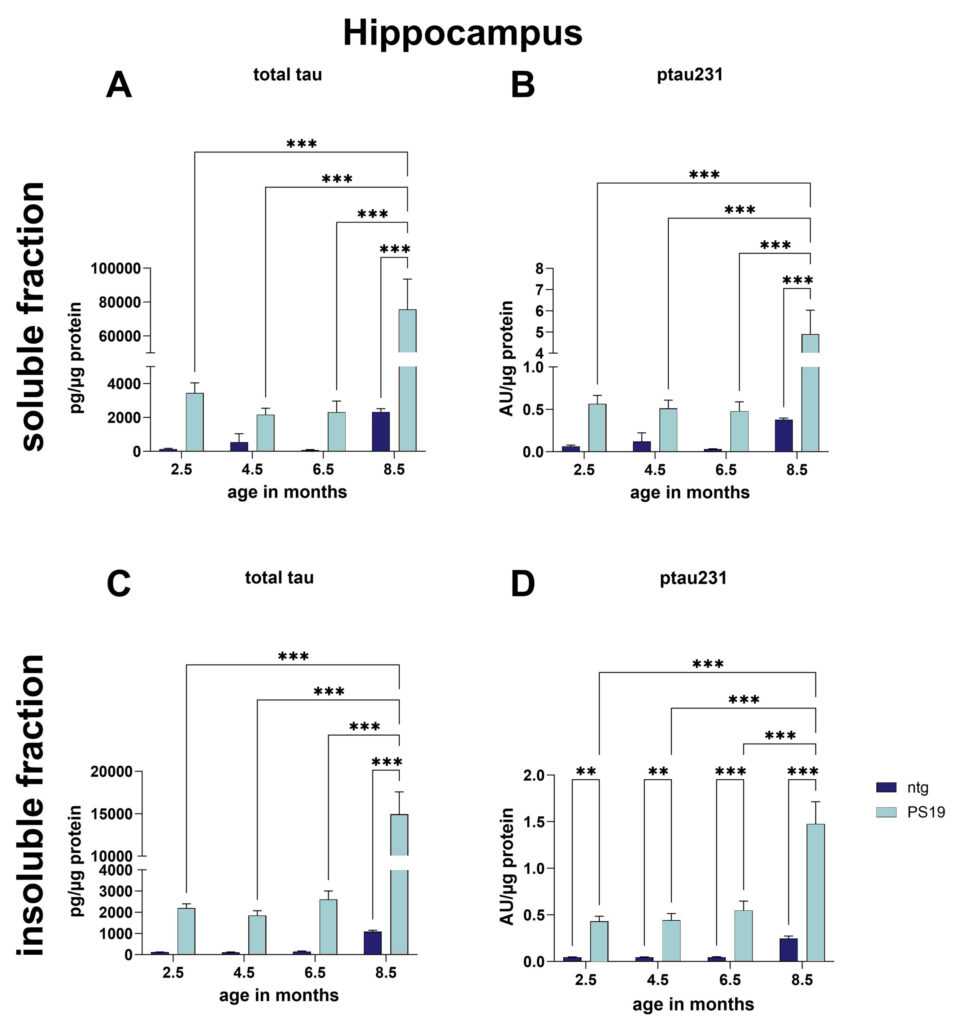
Figure 2: Total tau and ptau231 levels in the soluble and insoluble hippocampal fraction of PS19 and ntg mice at the age of 2.5, 4.5, 6.5, and 8 months. Immunosorbent assay for total tau and ptau231 in Triton X-100 soluble and insoluble fraction. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test. Mean + SEM; n = 8 / group; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
Together with our previous preliminary results showing increased total tau, ptau231, and ptau181 levels, our new results provide insights about the pathological progression in PS19 mice as model of tauopathies.
These results further promote PS19 mice as valuable tool to study tauopathies, tau phosphorylation, and to test new compounds for their efficacy to ameliorate tau-related diseases.
Further results about pathological changes of PS19 mice are currently being evaluated and will be presented soon. Stay tuned for more information about this mouse model for tauopathies!
Contact us today to get your study in PS19 mice started!








