In a previous newsletter we already introduced the AAV2 hA53T-α-syn mouse model to present increased hA53T-α-syn levels in the unilaterally virus-injected substantia nigra and the caudate putamen of the same hemisphere compared to the contralateral hemisphere injected with control vector. Furthermore, we could show decreased tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) levels and increased Iba1 levels in the substantia nigra of this model. These first analyses suggest that AAV2 hA53T-α-syn injected mice present a Parkinson’s disease-relevant hA53T-α-syn phenotype that is accompanied by a dopaminergic pathology and microgliosis.
We now evaluated the model in more detail for infiltrating cells in the substantia nigra of the AAV2 hA53T-α-syn-injected compared to the control hemisphere. Our results show a significantly increased object density of the leukocyte common antigen CD45 (Figure 1A), infiltrating T-cells by CD3 labelling (Figure 1B), as well as infiltrating cytotoxic T-cells by CD8 labelling (Figure 1C) in the AAV2 hA53T-α-syn-injected hemisphere.

Figure 1: Quantification of CD45, CD3, and CD8 in the substantia nigra of the AAV2-A53T-α-syn– and control-injected hemisphere. Four brain sections per mouse were analyzed. n = 8. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test (A and C); paired t-test (B). Mean ± SEM. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001. D: Representative images of the substantia nigra injected with control vector or AAV2-A53T-α-syn and labelled with antibodies against tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), CD8, and CD45 (left) or tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), CD8, and CD3. Both labellings were counterstained for nuclei with DAPI. SN: substantia nigra.
Additionally, oxidative stress could be observed as indicated by increased malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in the substantia nigra (Figure 2A) and caudate putamen (Figure 2B) in the AAV2 hA53T-α-syn-injected hemisphere.
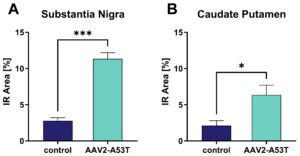
Figure 2: Quantification of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the substantia nigra and caudate putamen of the AAV2-A53T- and control-injected hemisphere. Five brain sections per mouse were analyzed. n = 8. Paired t-test (A), Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test (B). Mean ± SEM and means of the individual animals. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001.
The AAV2-hA53T-α-syn induced mouse model is thus characterized by a fast disease onset, a disturbed dopaminergic system, strong neuroinflammation, as well as increased oxidative stress. While some of these pathologies are only measurable in the AAV2-A53T-α-syn-injected substantia nigra, are the A53T-α-syn protein expression as well as oxidative stress also increased in the caudate putamen of the same hemisphere and thus indicating a systemic effect of the local AAV2 hA53T-α-syn injection.
Contact us today to get your study in the AAV2-hA53T-α-syn induced mouse model started!








