LPS-stimulated organotypic hippocampal slices provide an optimal tool to investigate the impact of developmental compounds on inflammasome activation in vitro.
By maintaining the three-dimensional structure and interplay of different cell types of the postnatal brain, this system closely resembles the in vivo situation while offering several advantages for early screenings:
- take supernatant samples anytime
- test new compounds without the challenge of BBB permeability
- semi high through-put
- Dexamethasone can serve as reference compound
The activation of the inflammasome can be monitored by assessing NLRP3 expression within the slice tissue and e.g. IL-1β release in the supernatant as shown below:
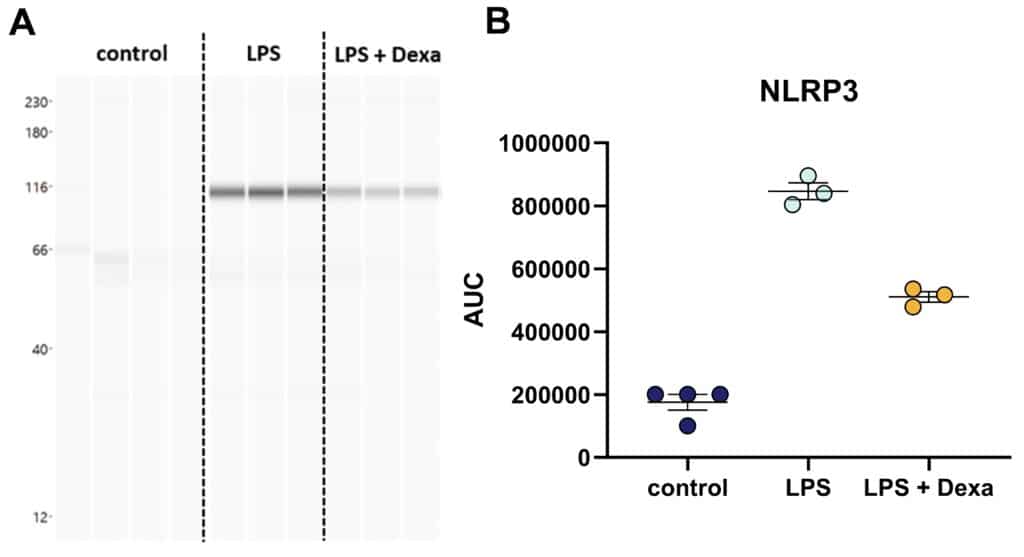
Figure 1: Quantification of NLRP3 in mouse hippocampal slices after LPS stimulation for 24 h. A: NLRP3 quantification of LPS-stimulated organotypic brain slices by an automated Western Blot system (WES). B: NLRP3 area under the curve (AUC) values of LPS-stimulated organotypic brain slices as measured by WES. Aligned dot blot; Mean ± SEM; n = 3 – 4 per group. Dexamethasone (Dexa) served as reference compound. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison post hoc test compared to LPS-treated group; ***p<0.001.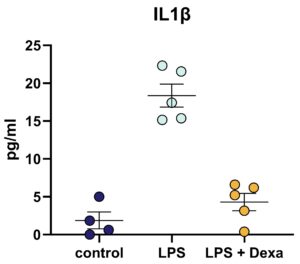
Figure 2: IL-1ß release by mouse hippocampal slices after LPS stimulation for 24 h. Aligned dot blot; Mean± SEM; n = 4 – 5 per group. Dexamethasone (Dexa) served as reference compound. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison post hoc test compared to LPS-treated group; ***p<0.001.
Contact us today to get your inflammasome study started!









