Reduced GCase activity is a key causative hallmark of Gaucher disease. Monitoring changes in GCase activity at multiple time points from small volumes of whole blood, sampled as dried blood spots (DBS), can give valuable new insights on drug effects.
Mutations in the human glucosylceramidase-β (GBA) gene and associated GCase activity are causative for Gaucher disease (GD). Beyond the significance of GCase for GD, the enzyme is highly discussed as therapeutic target in Parkinson`s disease research.
Translational read-outs to screen drug candidates or to test enzyme replacement- or gene therapy approaches in preclinical models are constantly developed and improved.
The use of DBS analyses, including the assessment of GCase activity, for diagnosing and monitoring GD in patients has emerged as the gold standard.
DBS offers a practical solution for clinical applications due to their minimal whole blood requirements, ease of storage, and transportability. The same advantages apply to animal studies; however, the challenges arise when working with even smaller blood volumes, making it more difficult to obtain consistent and reproducible results.
At Scantox, we optimized a 4-MUG-based GCase activity assay on DBS samples using only a minimal amount of whole blood. This approach enables the utilization of blood obtained from multiple in vivo samplings in mice to monitor GCase activity progressively, eliminating the dependency on single end-point measurements.
The following data provide a comparative analysis of GCase activity assessed in the brain (A) and DBS samples (B) derived from 4 months old GBA D409V KI mice, highlighting the concordance of these read-outs. Brain and DBS samples from homozygous (tm/tm), heterozygous (tm/wt), and wild type (wt/wt) littermates were analyzed, revealing a gene-dosage-dependent reduction in GCase activity in both sample types (see Figure 1).
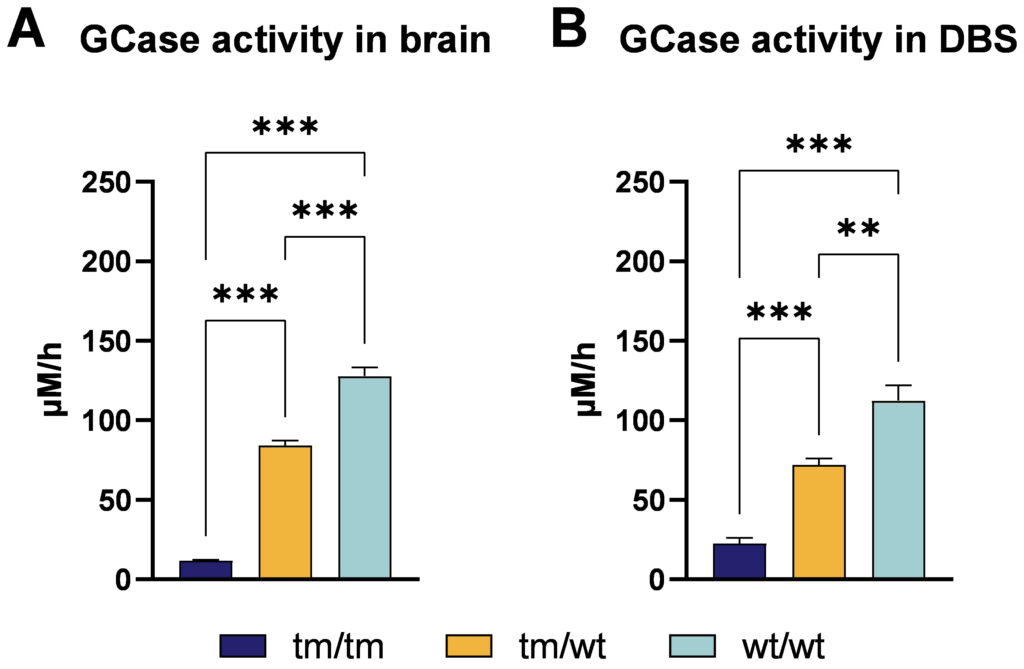
Figure 1: GCase activity in brain and DBS of GBAD409V KI mice. Brain and DBS samples of 4 months old homozygous (tm/tm), heterozygous (tm/wt) and wild type (wt/wt) littermates were analyzed using a 4-MUG-based assay. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons post hoc test; mean + SEM; n = 6 per group; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. tm, targeted mutation.
Contact us today to get your Gaucher disease study started!








