Newest results of our student’s FFG-funded PhD thesis at Scantox in cooperation with Prof. Marcello Leopoldo from the University of Bari, Italy, confirms the value of Fmr1-knockout (KO) mice to model neurobehavioral deficits manifested in fragile X syndrome.
Fragile X syndrome is the most commonly inherited form of intellectual disability and a monogenic cause of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Except for the cardinal symptoms of FXS, such as intellectual disability and sociability impairments, affected patients also manifest secondary phenotypic traits including hyperactivity, repetitive behavior, and aberrant emotional processing.
Behavioral analysis of Fmr1-KO mice revealed an increased activity and hyperactivity in Fmr1-KO mice as analyzed in the open field test (Fig.1A, B). In this test, Fmr1-KO mice also spent more time in the center of the arena compared to C57BL/6JRj control mice, indicating reduced anxiety-like behavior (Fig.1C). To validate this result, Fmr1-KO mice were further evaluated in the elevated plus maze. Results show a strongly reduced anxiety in Fmr1-KO mice compared to C57BL/6JRj control mice, as Fmr1-KO mice spent more time in the open arms of the maze and entered these open arms more frequently (Fig.1D-E).
Finally, our PhD student Shirin Sharghi evaluated the auto-grooming behavior of Fmr1-KO mice as a readout of repetitive behavior. Animals presented significantly more grooming episodes and spent significantly more time grooming itself compared to C57BL/6JRj control mice. Treating animals with the GABAergic drug R-Baclofen shortly before testing was able to reduce the auto-grooming behavior of Fmr1-KO mice to control levels (Fig.2A, B).
In conclusion, Shirin was able to show that Fmr1-KO mice present significant changes in activity, hyperactivity, anxiety, and repetitive behavior and that the latter can be ameliorated by acute treatment with R-Baclofen.
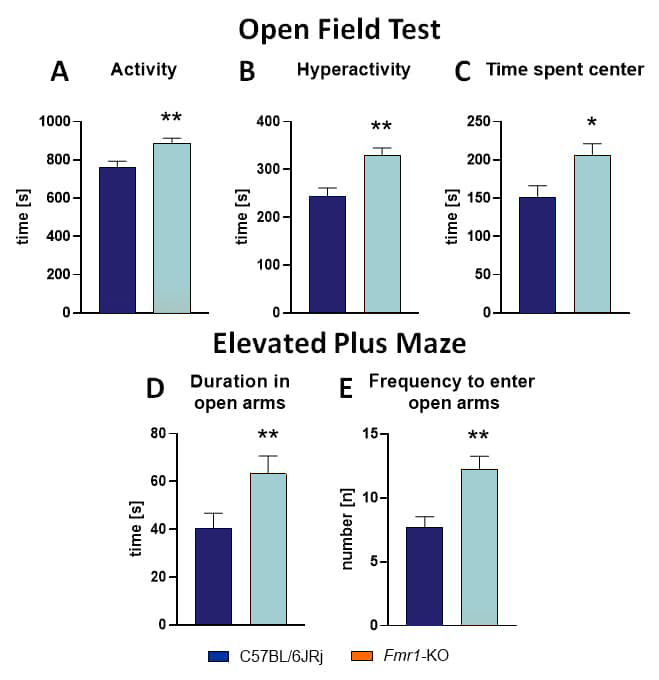
Figure 1: Activity, hyperactivity, and anxiety in male Fmr1-KO mice at the age of 7 weeks compared to C57BL/6JRj control mice. Activity (A), hyperactivity (B), and time spent in the center (C) as measured in the open field test. Duration spent in open arms (D), and frequency to enter open arms (E) as measured in the elevated plus maze test. n = 15 per group. Unpaired t-test; mean + SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
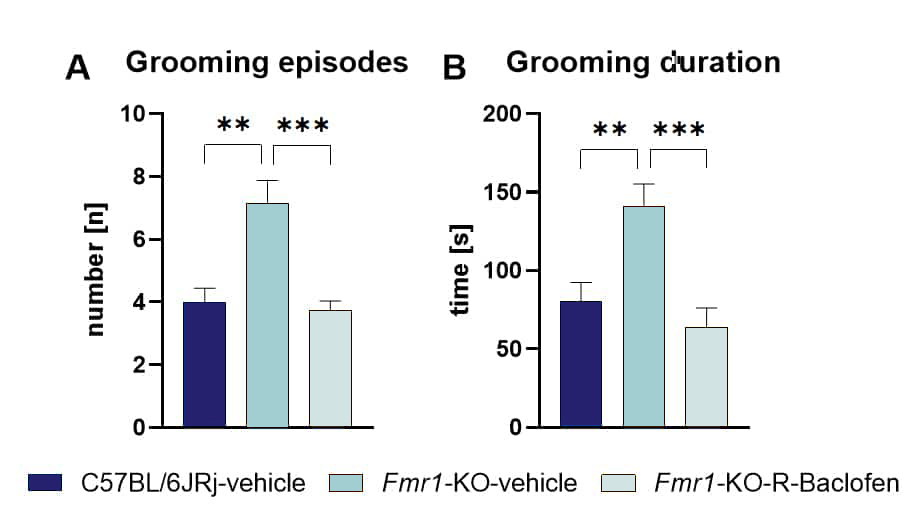
Figure 2: Auto-grooming of male Fmr1-KO mice after R-Baclofen or vehicle treatment at the age of 7 weeks. Number of grooming episodes (A) and grooming duration (B) of Fmr1-KO mice and C57BL/6JRj control mice. n = 15 per group. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test; mean + SEM; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
Contact us today to get your Fmr1-KO mouse study started!








